Food-grade industrial pumps
Buying guide & technical applications
In the food and beverage industry, selecting the right transfer pump is a strategic decision. An unsuitable pump can compromise product quality, slow down production, and generate unnecessary costs. This professional buying guide presents the most effective pumping solutions for food-grade liquids, viscous products, fluids with solid particles, and sensitive materials. Whether you're involved in winemaking, sauce production, or dairy processing, you'll find the industrial food pump that fits your needs right here.
FOOD TRANSFER PUMPS : A CRITICAL DECISION FOR YOUR PROCESS
A well-selected pump ensures hygienic, fast, and efficient product transfer, while meeting the specific requirements of viscosity, temperature, and fluid sensitivity. Choosing the right food-grade industrial pump is a smart investment — it enhances production performance, reduces losses, and guarantees sanitary compliance.
TECHNICAL CRITERIA FOR SELECTING A FOOD-GRADE PUMP
- Product viscosity
Pumps handling viscous products must deliver a steady flow without pressure loss. - Solid particles
Choose a pump designed to handle solids without clogging. - Delicate materials
Peristaltic or lobe pumps enable gentle, shear-free transfer. - Hygiene & standards
Pumps must comply with MOCA, 3-A, or FDA standards.
INDUSTRIAL FOOD PUMPS : TYPES & APPLICATIONS
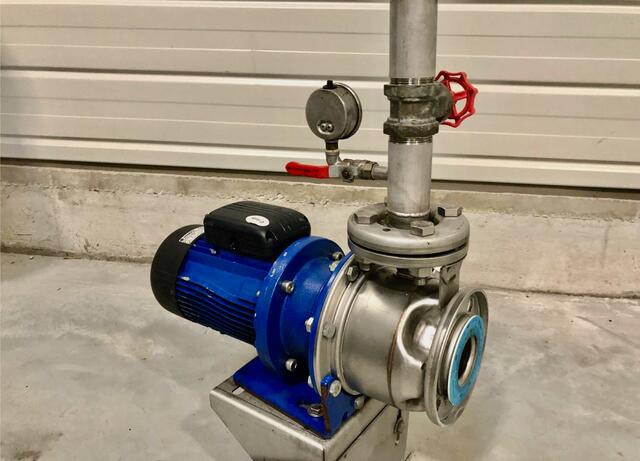
Centrifugal Pumps – For Clear Liquids
- Applications : juice, water, wine
- Benefits : high flow rate, cost-effective, easy to clean
- Limitations : not suitable for viscous products or those with solid particles
Centrifugal pumps play a key role in food processing operations, particularly for fluid transfer, feeding filtration systems, and thermal treatment stages. Their operating principle relies on a high-speed rotating impeller that generates centrifugal force to move low- to medium-viscosity liquids efficiently—such as water, juices, broths, or other homogeneous food-grade fluids.
Their design enables high and continuous flow rates, making them ideal for automated production lines that require consistent and smooth product feeding. In filtration systems, centrifugal pumps help maintain steady upstream pressure, which improves fine particle separation and ensures the clarity of finished products.
Typically made from stainless steel—often 316L grade—these pumps offer excellent corrosion resistance and full compatibility with CIP (Clean-in-Place) systems, meeting the strict hygiene standards of the food industry. They also tolerate high temperatures, making them suitable for thermal processes such as pasteurization and sterilization. However, precise flow and pressure control in such applications depends on external regulation devices (sensors, valves, PLCs), as the pump itself does not provide fine-tuned modulation.
Their hygienic construction and chemical inertness help minimize contamination risks and preserve the organoleptic and microbiological integrity of products—provided the entire pumping system is properly designed and maintained.
In summary, centrifugal pumps offer a reliable, cost-effective, and hygienically compliant solution for transferring clear food-grade liquids in modern production environments.

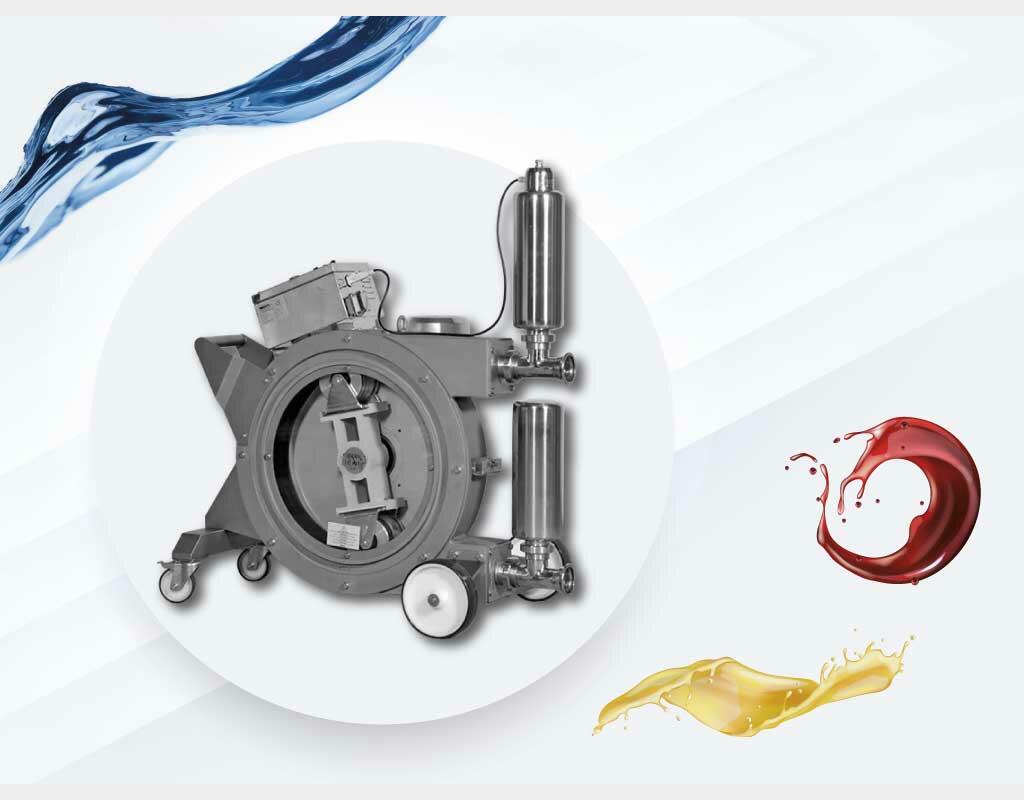
Peristaltic Pumps – For Sensitive Products
- Applications : purées, compotes, creams
- Benefits : gentle transfer, excellent product integrity
- Limitations : higher cost, requires regular maintenance
Peristaltic pumps offer a highly effective transfer solution tailored to the demands of the food processing industry, especially for sensitive, viscous products or those containing particles. These pumps operate by gradually compressing a flexible tube with a rotating roller, allowing the fluid to move without direct contact with the pump’s mechanical components. Only the inner surface of the hose comes into contact with the product, significantly reducing the risk of cross-contamination and simplifying cleaning procedures.
In environments equipped with stainless steel tanks and subject to strict hygiene requirements, this technology integrates seamlessly — particularly due to its compatibility with clean-in-place (CIP) and, depending on the hose type, sterilize-in-place (SIP) protocols. While sterility is not inherently ensured by the pump alone, its closed and minimalist design supports a highly hygienic and controlled process environment.
Peristaltic pumps excel in dosing and filling operations, where they deliver controlled flow rates and high repeatability. This precision makes them ideal for packaging viscous products in various container formats (bottles, jars, pouches), as well as for the accurate addition of functional ingredients such as flavors, colorants, or additives — all while complying with strict formulation standards.
These pumps can handle a wide range of viscosities, including products with soft or small particles (e.g., fruit pieces, grain suspensions, textured purées), provided the hose is properly sized to prevent crushing or blockage. The absence of valves or seals minimizes retention zones and drastically reduces shear, helping preserve the physical and organoleptic qualities of sensitive products.
In summary, peristaltic pumps are a reliable and precise technology for transferring and dosing delicate food products. Their gentle operation, inherent cleanliness, and adaptability make them a top choice for production lines requiring performance, hygiene, and respect for product integrity.
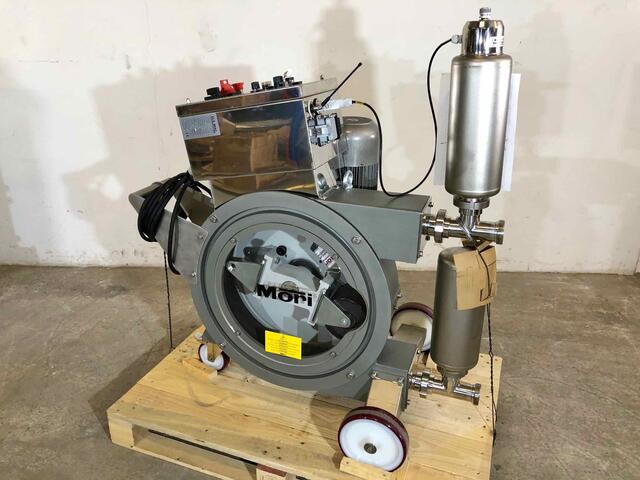

Pomace Pumps – For Solid Residues
- Applications : winemaking, juice extraction, olive oil production
- Benefits : solid-handling capability, robust design, continuous transfer
- Limitations : requires proper sizing, clogging risk if poorly maintained
Pomace pumps play a crucial role in many food processing sectors where handling solid by-products is a regular part of production. Specifically engineered to transfer solids such as skins, seeds, fibers, or olive pulp, these pumps help maintain process continuity while reducing the need for manual intervention.
One of their key functions is to transfer pomace from processing tanks to downstream steps like pressing or secondary extraction. In winemaking, olive oil production, or fruit juice industries, pomace is a heterogeneous and often viscous mass that requires robust equipment suited for solid transfer. These pumps ensure efficient flow, provided the pump type is correctly matched—whether progressive cavity, piston, or lobe pump—to the particle size, viscosity, and required flow rate.
Pomace pumps are also used to evacuate solid residues at the end of processing cycles. Their design allows the passage of solids without prior grinding, significantly reducing blockage risks when properly sized and maintained. Using feed hoppers or augers upstream can further enhance their performance.
Although their primary role is solid transfer, some pomace pumps can assist in draining residual liquids (such as juice or must) from the pomace, complementing decanting or pressing systems. It’s important to note, however, that these pumps do not replace mechanical presses—they are designed to move semi-liquid materials efficiently, minimizing air exposure and oxidation risk, as long as pumping parameters are well controlled.
The efficiency of a pomace pump relies on precise sizing based on the product's characteristics: solids content, abrasiveness, viscosity, particle size, and more. Material selection—especially for seals, gaskets, and contact parts—must also meet strict hygiene requirements for food applications. Contrary to popular belief, compatibility with stainless steel tanks is not the primary concern; it’s the compatibility between the pump and the product that ensures safe, hygienic, and durable operation.
Pomace pumps are a vital technical solution for managing solid by-products across multiple food industries. When properly selected and applied, they streamline production, reduce manual handling, and add value by optimizing co-product recovery. To ensure long-term performance and reliability, their selection should be based on a thorough analysis of the product to be transferred and the specific demands of the process.

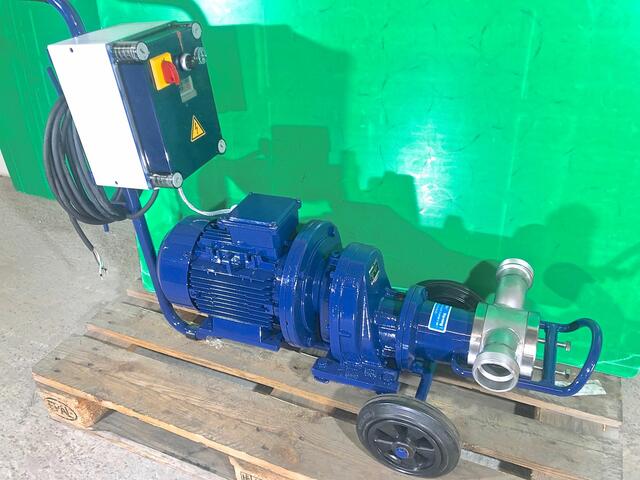
Flexible impeller pumps in the food processing industry
- Applications : transfer of clear liquids, loop circulation, cleaning
- Advantages : stable flow rate, good self-priming capacity, compact design
- Limitations : not suitable for viscous fluids or precision dosing
Flexible impeller pumps, also known as rotary vane pumps, are used in specific applications within the food industry — particularly for transferring clear or low-viscosity liquids. Their design features a flexible rotor rotating inside a stator, compressing and moving the fluid with consistent flow. This simple mechanism provides excellent self-priming capability and smooth operation at low pressure.
These pumps are especially effective for handling free-flowing liquids such as water, filtered juices, light vegetable oils, or mildly concentrated syrups. They deliver a relatively constant flow, making them well-suited for quick transfers between tanks, pipes, or heat exchangers. However, they are not designed for viscous, pasty, or particulate-laden products, which may damage the flexible rotor or reduce efficiency.
In some settings, these pumps are also used for liquid recirculation — notably in cooling systems or clean-in-place (CIP) processes. Their easy priming and stable low-pressure performance make them a good fit for such tasks. That said, when working with large volumes or very cold fluids, centrifugal pumps are often preferred.
Unlike other technologies such as peristaltic or positive displacement pumps, flexible impeller pumps are not recommended for precise dosing or container filling. Their volumetric tolerance is relatively wide, and flow rates may fluctuate depending on back pressure, making them less reliable for applications requiring exact quantities.
In food processing environments, these pumps are typically paired with stainless steel tanks or production lines, ensuring good hygiene and chemical compatibility with the handled liquids. It is essential, however, to select food-grade versions made from corrosion-resistant, easy-to-clean materials that comply with sanitary standards.
Flexible impeller pumps offer a simple and reliable solution for transferring low-viscosity liquids in food industry applications — provided their technical limits are respected. They are ideal for transfer and circulation tasks, but should not be confused with technologies better suited for sensitive, viscous products or operations requiring precise dosing. As always, the right pump choice depends on a thorough analysis of the fluid's properties and the process requirements.

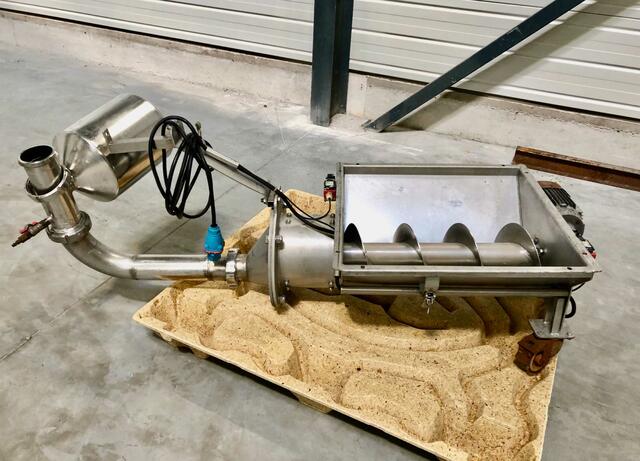
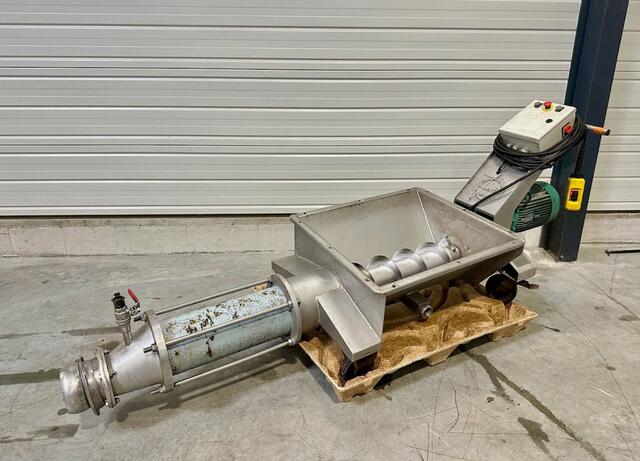
Progressive cavity pumps (also known as eccentric screw pumps)
- Applications : purées, pastes, thick sauces, mixtures with solid particles
- Benefits : gentle transfer, consistent flow rate, effective for viscous or chunky products
- Limitations : not designed for active mixing – requires precise sizing
In the food industry, transferring viscous, thick, or particle-loaded products often presents complex challenges. Progressive cavity pumps — also known as eccentric screw pumps — offer a highly effective technical solution for such applications.
These pumps are particularly well suited for high-viscosity products such as purées, thick sauces, pasta mixtures, or blends containing fruit, vegetable, or meat pieces. Thanks to a helical rotor operating within an elastomer stator, they generate a smooth, non-pulsating flow and maintain continuous transfer even at low speeds. This technology helps preserve the integrity of the product, provided the pump is correctly sized and the rotation speed is properly set. Depending on the particle size and shear sensitivity, these pumps can move product without damaging it — a key factor in maintaining the visual and sensory quality of the final product.
While they are not designed for active ingredient mixing, progressive cavity pumps can help maintain homogeneity during transfer. By preventing phase separation or sedimentation in the lines, they play an essential role in intermediate production steps where consistent texture must be preserved.
Installed alongside stainless steel tanks, these pumps meet the strict hygiene and cleaning requirements of the food industry. Models built for food processing use compliant materials and are often compatible with CIP (clean-in-place) protocols, ensuring safe and contamination-free production.
Progressive cavity pumps provide a reliable, durable, and product-friendly solution for handling complex fluids in food processing environments. Their ability to manage viscous or particle-filled products, combined with steady flow control via variable speed drives, makes them a preferred choice in many applications. However, optimal performance and durability require careful attention to sizing, rotational speed, and the nature of the product being pumped.

Winemaking Pump Guide : Transferring Wine and Pomace
In the winemaking industry, mastering the transfer of liquids and solids is essential to preserving the final product’s quality and optimizing operations in the winery or cellar. Choosing the right pump ensures compliance with food safety standards while enabling gentle and efficient handling of each stage — from must to finished wine and pomace.
Available types of winemaking pumps
Selecting the appropriate pump is critical to maintaining wine quality throughout the entire vinification process. Below are the main pump types commonly used in wineries :
- Wine pump – For transferring must or clear wine.
- Pomace pump – Designed to handle solid residues from fermentation.
- Grape pump – Suitable for whole or destemmed grapes.
- Progressive cavity pump (also known as ‘pig-tail’ pump) – Ideal for viscous products or mixtures containing solids.
- Peristaltic pump – Particularly recommended for the gentle transfer of delicate products.
- Centrifugal pump – Used for clear liquids or cleaning applications.
🔍 Note : Impeller pumps are rarely used in winemaking, except for auxiliary tasks such as transferring water or cleaning agents.
Which pump for which winemaking process ?
- Grape transfer → Progressive cavity pump
Ideal for crushed or destemmed grapes, it preserves the integrity of the fruit and prevents excessive crushing. - Gentle transfer of must or wine → Peristaltic pump
Thanks to its low-shear operation and the absence of direct mechanical contact, it protects the structure of the wine, as well as the yeast and aroma compounds. - Equipment cleaning → Stainless steel centrifugal pump
Ensure correct connections, power supply specifications, flow/pressure capacity, and integration with existing systems.
Buying a used wine pump : key considerations
Purchasing a used wine pump can be a cost-effective option — provided the following points are carefully checked :
- Condition of wear parts :
Seals, gaskets, membranes, hoses, or lobes depending on the pump type. - Compliance with food-grade standards :
All product-contact materials (stainless steel, elastomers) must meet relevant hygiene requirements. - Technical documentation :
Check for manuals, schematics, CE certifications, and flow curves. - Technical compatibility :
connexions, alimentation électrique, capacité en débit/pression, intégration aux lignes existantes.
—
ARSILAC stocks fully reconditioned pumps, covered by a 6-month warranty — a smart investment with peace of mind.
—
focus on industrial food-grade pumps : types & use cases
Clean-in-Place (CIP)
CIP is an essential procedure to ensure the hygiene of production lines. It allows automated pump cleaning without disassembly, effectively removing residues and microorganisms.
Wear part monitoring
Certain components are subject to mechanical or chemical wear and must be monitored regularly:
- Tubing (peristaltic pumps)
- Membranes (diaphragm pumps)
- Lobes (rotary lobe pumps)
Timely replacement prevents unexpected downtime.
Preventive Maintenance
A scheduled maintenance program helps :
- Extend pump lifespan
- Lower operating costs
- Prevent critical failures
Peristaltic, centrifugal, impeller and pomace pumps play a key role in the food industry, ensuring efficient liquid transfer while preserving product quality.
The use of stainless steel tanks guarantees optimal hygiene and helps prevent contamination throughout the process. By selecting the right pump based on the liquid’s properties and the specific needs of the application, food and beverage producers can improve efficiency, boost productivity, and maintain product integrity.
✖ Unsure whether your project is feasible ?
Feel free to contact an ARSILAC advisor if you have any questions or would like more information on the different pump types used in the food industry. We’ll help you identify the pumping solution that fits your needs.
#pump #foodindustry #transfer #peristalticpump #industrialpumping #stainlesssteelequipment
_
Note : This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute professional advice. We recommend consulting industry experts and following applicable regulations for your specific process.