What material should I choose for an industrial storage tank?
Fibreglass, stainless steel or steel :
Which composition is suitable for your industrial sector ?
Choosing the material for an industrial storage tank is a strategic decision with significant implications. Whether stainless steel, fibreglass, epoxy or coated steel, this choice directly impacts durability, resistance and compatibility with the substances stored. In sectors as diverse as agri-food, chemicals and water treatment, selecting the optimal material is key to ensuring the performance, safety and longevity of your industrial tanks.
How to choose the right material for your industrial tank ?
Before choosing the material for your tank, ask yourself the following questions :
- Nature of the content
What substance will the tank contain? (liquids, solids, gases, chemicals, etc.) - Chemical propertiess
Are the substances corrosive, reactive, or do they have specific chemical compatibility requirements ? - Terms of use
What are the expected operating conditions? (temperature, pressure, external environment, etc.) - Standards and regulations
What industry standards or regulations must be complied with ? - Sustainability and safety
What is the desired service life, and what are the safety requirements ? - Cost
What are the costs associated with each material, including manufacturing, maintenance, and replacement ?
The choice of material directly influences the quality, safety and regulatory compliance of your products. Choosing the right material reduces the risk of contamination, extends the service life of tanks and ensures compliance with the most stringent industry standards.

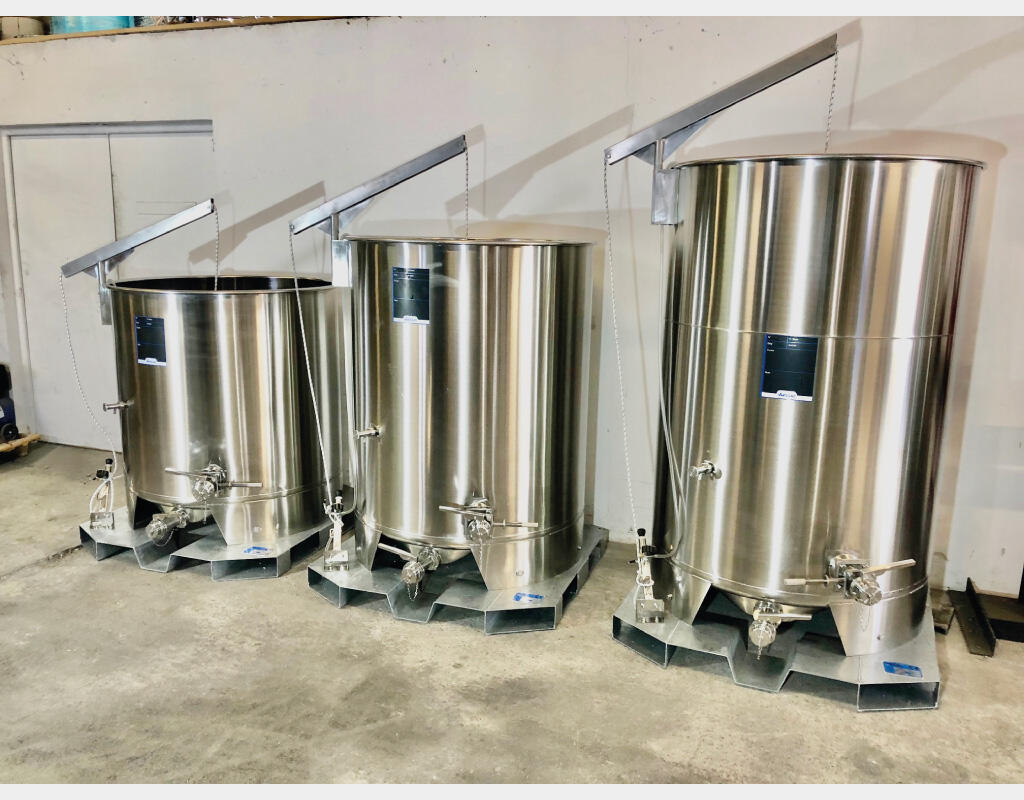
The determining factors for choosing the tank material
Corrosion resistance
Concept : Health and regulatory standards define the minimum requirements for materials that come into contact with food or chemical products. These standards guarantee that there is no risk to health.
Importance : Failure to comply with these standards may result in penalties. Stainless steel tanks are often preferred in the food industry because they are non-toxic, easy to clean and do not encourage bacterial growth.
Mechanical properties and durability
Concept : Mechanical properties, such as pressure resistance, ductility and impact resistance, determine a tank's ability to withstand stress without deforming or cracking. Durability measures the material's ability to maintain its properties over time.
Importance : Tanks are often subjected to harsh conditions. Choosing a robust material, such as stainless steel, ensures the safety and structural integrity of the tanks.
Ease of cleaning and maintenance
Concept : In the food industry, hygiene is crucial. Materials must be easy to clean thoroughly to prevent cross-contamination. Surfaces must be smooth, non-porous and resistant to cleaning products.
Importance : A material that is easy to clean reduces the risk of contamination. Stainless steel, for example, is often used because it is non-porous and can be sterilised.
The materials of choice for industrial tanks : fibreglass, stainless steel and steel
Here is a comparative overview of the materials commonly used for industrial tanks, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages :
Steel (epoxy/coated)
- Composition : Mild steel is a low-carbon steel, typically containing 0.05% to 0.25% carbon by weight.
- Corrosion resistance: Low. It requires protective coatings (such as galvanisation, paint or epoxy) to prevent rust and corrosion, especially in harsh environments.
- Strength : High tensile strength but lower than stainless steel.
- Durability : Good, but susceptible to corrosion and requires regular maintenance to ensure longevity.
- Weight : (heavy). The tanks are significantly heavier than fibreglass tanks, which makes them more difficult to transport and install.
- Thermal conductivity (high). Tanks can conduct and transfer heat quickly, which may not be desirable in all applications.
- Cost : Generally the cheapest option. However, the cost of maintenance and protective coatings must be taken into account.
- Applications : Used in applications where cost is a major concern and where the environment is not highly corrosive, such as water, oil and gas storage and certain industrial processes.
- Maintenance : Low maintenance requirements thanks to inherent corrosion resistance.
- Lifespan : Very long lifespan, often several decades with proper care.
- Environmental impact : Steel production has a significant environmental footprint due to the energy-intensive processes involved.
💡 Economical but requires regular maintenance due to its susceptibility to corrosion.
Stainless steel
- Composition : Stainless steel contains chromium (at least 10.5%) and other elements such as nickel, molybdenum and manganese.
- Corrosion resistance : Excellent. Stainless steel is inherently resistant to rust and corrosion due to the presence of chromium, which forms a passive layer of chromium oxide.
- Strength : Very high tensile strength.
- Durability : Excellent. Stainless steel tanks can last for decades with minimal maintenance due to their corrosion resistance and high strength.
- Weight : (heavy). Similar to steel tanks, stainless steel tanks are also heavy, but slightly lighter than epoxy-coated or coated steel tanks due to their higher strength-to-weight ratio.
- Thermal conductivity : lower than that of steel but still conducts heat relatively well.
- Cost : More expensive than steel. The high initial cost is often offset by lower maintenance costs and a longer service life.
- Applications : Ideal for food and beverage processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and applications involving corrosive substances or high temperatures.
- Maintenance : Low maintenance requirements thanks to inherent corrosion resistance.
- Lifespan : Very long lifespan, often several decades with proper care.
- Environmental impact : Also has a considerable environmental impact, but stainless steel is 100% recyclable, which can mitigate its overall footprint.
💡High initial cost but offers excellent durability, low maintenance and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Fibreglass and polyethylene
- Composition : FRP is made from a polymer matrix (such as polyester, vinyl ester or epoxy) reinforced with fibres (usually glass fibres).
- Corrosion resistance : exceptional. PRF is highly resistant to corrosion caused by chemicals, water and other environmental factors, making it ideal for harsh and corrosive environments.
- Strength : high strength-to-weight ratio. Although less resistant to traction than stainless steel, it is sufficiently strong for most industrial applications.
- Durability : Highly resistant to corrosive environments. However, mechanical damage may affect its structural integrity.
- Weight : (lightweight). FRP tanks are much lighter than MS and SS tanks, reducing transport and installation costs.
- Thermal conductivity : (very low). PRF is an excellent insulator, making it suitable for applications where thermal insulation is required.
- Cost : comparable or slightly higher than stainless steel, depending on the application and resin used. Its cost is justified by its excellent corrosion resistance and low maintenance requirements.
- Applications : Ideal for chemical storage, wastewater treatment, marine environments, and any application requiring resistance to corrosive substances and harsh environmental conditions.
- Maintenance : Minimal maintenance is required. Periodic inspections to detect any mechanical damage are recommended.
- Lifespan : Long lifespan, particularly in corrosive environments.
- Environmental impact : The production of PRF involves the use of chemicals and resins that can be harmful if not managed properly. However, the long service life and low maintenance requirements of PRF can partially offset its environmental impact.
💡Offers excellent corrosion resistance, is lightweight and requires little maintenance. Ideal for highly corrosive environments, but can be more expensive initially.

Choosing the material for an industrial tank is a strategic decision that requires in-depth analysis of numerous factors, including the nature of the substances stored, environmental conditions, budget and maintenance capabilities. From the nature of the substances stored to operational conditions and regulatory requirements, each element must be carefully weighed. Although stainless steel often stands out for its versatility, strength and hygienic qualities, other materials such as fibreglass or engineering plastics ma
By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each material, you can make an informed decision that best meets the needs of your specific application. The optimal choice will depend on your unique requirements and the particularities of your industry. A thoughtful investment in the right material will not only ensure the performance and safety of your tanks, but also their long-term cost-effectiveness.
✖ Doubts about the feasibility of your project ?
Please do not hesitate to contact an Arsilac representative if you have any questions or would like more information about the types of equipment suited to your production profile. Find the solution that meets your needs.
FAQ
Q1 : How do steel tanks compare to plastic tanks for water storage ?
They offer superior durability and a longer service life than plastic ones. Stainless steel tanks are UV-resistant and retain their structural integrity better than polyethylene tanks. However, plastic rainwater tanks are often less expensive and more impact-resistant.
Q2 : Are stainless steel water tanks rustproof ?
Stainless steel tanks are more resistant to rust than carbon steel tanks. Different types of stainless steel tanks offer varying levels of corrosion resistance. Proper welding and regular maintenance help prevent rusting in stainless steel tanks.
Q3 : How do environmental conditions affect the choice of stainless steel tanks ?
Marine environments favour stainless steel tanks due to their resistance to salt water. Polyethylene tanks may be preferable in cases of extreme temperature variations due to their flexibility. Consider the local climate and water quality when choosing between rust-resistant stainless steel tanks and plastic tanks.
Q4 : What are the cost differences between steel and plastic tanks ?
These tanks have a higher initial cost, but often prove to be more cost-effective in the long run due to their durability. Plastic tanks offer a lower initial investment, making them attractive for tight budgets. When comparing options, consider the lifespan and maintenance costs.
#tank #industry #fibre #stainless steel #steel #storage #optimisation
_
Note: This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute professional advice. It is recommended that you consult with experts and comply with the specific regulations of each industry.